Unraveling the Intricacies of the Human Hand's Bones: An In-Depth Exploration


Animal Species Profile
The human hand, a marvel of evolution, stands as a testament to the intricate design and functionality of bones on hand. Delving deep into the anatomy of this vital skeletal structure reveals a complex interplay of bones, tendons, and ligaments that enable our hands to perform a multitude of tasks with precision and dexterity. The physical characteristics and appearance of the bones on hand highlight their adaptability and versatility in various activities, from delicate grasping to powerful gripping.
Conservation & Wildlife Efforts
While the focus is on human hands in this exploration, it is crucial to acknowledge the importance of hand conservation in various species across the animal kingdom. Threats to hand structures, such as injuries or debilitating conditions, necessitate conservation initiatives and medical interventions to preserve hand functionality and mobility. Success stories of hand restoration surgeries showcase the impact of advancements in medical science on enhancing the quality of life for individuals facing hand-related challenges.
Animal Behavior & Psychology
In studying the bones on hand, we must also consider the behavioral and psychological aspects intertwined with hand usage. Communication cues through gestures and hand movements hold significance in human interaction, reflecting cognitive abilities and emotional expressions. Understanding the psychology behind hand gestures offers insights into social dynamics and empathy, underscoring the intricate connection between hands and human behavior.
Unique Facts & Trivia
Unveiling intriguing details about the bones on hand unveils lesser-known facts and trivia that add to the fascination of this anatomical wonder. From the hand's involvement in intricate tactile sensations to its role in fine motor skills, exploring the complexities of hand anatomy reveals surprising adaptations and functionalities. Discovering record-breaking feats achieved through hand-related activities showcases the remarkable potential and capabilities encoded within this seemingly ordinary yet extraordinary skeletal structure.
Pet Care & Tips
While human hands take the spotlight in this examination, reflecting on hand care resonates with pet owners, emphasizing the importance of paw and hoof care for domestic animal companions. Tips on grooming, nail trimming, and maintaining optimal hand health transition into practical advice for pet owners looking to enhance the well-being of their furry friends. Educating pet owners on the significance of hand hygiene and care routines contributes to fostering a nurturing environment for animal companions.";
Introduction to Bones On Hand
The intricate exploration of bones on hand delves into the fundamental structures that form this essential part of the human anatomy. Understanding the nuances of hand bones is pivotal for grasping the intricate mechanisms behind the hand's dexterity and functionality. As we journey through the depths of hand bones, we unravel the intrinsic connection between skeletal composition and hand movements. Through this detailed analysis, readers will gain a profound insight into the pivotal role that hand bones play in human anatomy and functionality.
Anatomical Overview of Hand Bones
Metacarpal Bones:
Within the realm of hand anatomy lies the Metacarpal Bones, crucial components that support the palm and connect it to the fingers. These bones provide structural integrity to the hand, facilitating grasping and manipulation tasks. Their unique feature lies in the length and arrangement, enabling the dexterity needed for intricate hand movements. Despite their robust nature, Metacarpal Bones can be susceptible to fractures under excessive force, affecting hand functionality.
Phalanges:
The Phalanges, comprising the fingers and thumb bones, are integral to hand mobility and precision grip. Their slender structure allows for precise movements essential for fine motor skills. The Phalanges exhibit a delicate balance between flexibility and stability, enabling varied hand gestures and functionalities. However, their size and position make them prone to fractures and dislocations, impacting everyday hand usage.
Carpal Bones:
Nestled within the wrist, the Carpal Bones form the intricate bridge between the forearm and hand. Their unique arrangement allows for a wide range of hand movements while maintaining stability and support. The compact nature of Carpal Bones ensures efficient transmission of force from the arm to the hand. Despite their crucial role in hand mechanics, Carpal Bones are vulnerable to trauma and degenerative conditions, affecting wrist mobility.
Structural Composition of Hand Bones
Cortical Bone:
Cortical Bone, denoting the dense outer layer of bones, contributes to the strength and rigidity of hand skeletal structure. Its high mineral content provides durability and resistance to bending forces, crucial for sustaining hand movements. The compact nature of Cortical Bone offers protection to vital structures within the hand. However, reduced flexibility may predispose it to fractures under sudden impact, necessitating caution during activities.
Trabecular Bone:
As the spongy inner layer of bones, Trabecular Bone imparts resilience and shock absorption to the hand skeleton. Its porous structure enhances the bone's capacity to withstand compressive forces, crucial for joint stability. The unique network of trabeculae within Trabecular Bone optimizes weight distribution and facilitates bone marrow production. Despite its impact-absorbing properties, Trabecular Bone may be prone to weakening with age or hormonal imbalances.
Bone Marrow:
Rich in hematopoietic stem cells, Bone Marrow serves as the vital core of hand bones, contributing to blood cell formation and immune function. Its fatty and hematopoietic components play a critical role in maintaining bone health and structural integrity. The regenerative capacity of Bone Marrow aids in repairing bone damage and supporting overall hand function. However, disruptions in bone marrow production can lead to hematologic disorders or compromised bone strength.
Functionality of Hand Bones
As we delve into the complex realm of bones in the hand, understanding their functionality is paramount. The intricate interplay of structures within the hand allows for a multitude of essential tasks. From grasping and manipulation to providing support and ensuring mobility, the hand bones are integral for daily activities. Their significance extends beyond mere physical tasks, contributing to fine motor skills, proprioception, and tactile sensitivity. By exploring the functionality of hand bones, we gain a profound appreciation for their role in human dexterity and interaction with the environment.
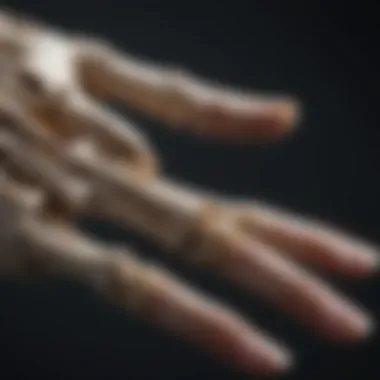

Grasping and Manipulation
Precision Grip
Precision grip, a fundamental aspect of grasping and manipulation, involves the coordination of fingers and thumb to handle objects delicately. This grip enables activities requiring precision and finesse, such as writing, picking up small items, or intricate crafts. The key characteristic of precision grip lies in the opposition between the index finger and thumb, allowing for pinpoint accuracy and control. While advantageous for tasks demanding accuracy, precision grip may exert strain on the hand after prolonged use. Despite its limitations, precision grip remains a popular choice for activities necessitating meticulous handling.
Power Grip
In contrast to precision grip, power grip emphasizes strength and force when grasping objects. This versatile grip engages multiple fingers and the palm to provide a firm hold on items of various sizes and shapes. The primary characteristic of power grip is the distribution of pressure across the hand, enhancing grip stability and endurance. Widely favored for tasks requiring strength, such as lifting heavy objects or twisting jar lids, power grip offers efficiency in handling robust materials. However, extended use of power grip can lead to fatigue and reduced fine motor control.
Support and Mobility
Articulations
Articulations play a crucial role in the support and mobility of hand bones, facilitating smooth movements and transitions. These joints connect the different bones of the hand, enabling flexibility and a wide range of motion. The key characteristic of articulations lies in their ability to absorb shock and distribute forces evenly during hand movements. This feature enhances joint stability while allowing for intricate finger movements essential for fine motor tasks. Despite their advantages in mobility, certain articulations may be susceptible to injuries or degenerative conditions.
Range of Motion
The range of motion in the hand reflects its adaptability and agility in various activities. This flexibility enables the hand to perform diverse tasks, from intricate finger movements to grasping objects of different shapes and sizes. The key characteristic of hand range of motion is its adaptability to varying functional demands. By adjusting to different grip styles and hand positions, the hand effectively carries out tasks with precision and efficiency. However, restricted range of motion can impede daily activities and impact overall hand function, highlighting the importance of maintaining optimal mobility.
Protection and Stability
Shock Absorption
Shock absorption is a vital function of hand bones, safeguarding the delicate structures during impact and heavy loads. This mechanism reduces the transmission of excessive forces to the bones and joints, minimizing the risk of fractures or injuries. The key characteristic of shock absorption is its ability to dissipate energy across the hand evenly, protecting vulnerable tissues. While beneficial for cushioning against external forces, excessive reliance on shock absorption alone may lead to joint overuse and soft tissue strain. Balancing shock absorption with other protective measures is essential for maintaining hand integrity.
Joint Stability
The stability of hand joints is crucial for maintaining proper alignment and functionality during intricate movements. By promoting joint cohesion and alignment, stability ensures optimal support for everyday tasks. The key characteristic of joint stability is its role in preventing excessive joint movements and reducing the risk of dislocations or sprains. A stable joint provides a reliable anchor for muscle contractions and coordinated movements, enhancing overall hand performance. However, over-reliance on joint stability without addressing muscle imbalances or structural weaknesses may lead to joint stiffness and decreased mobility.
Significance of Hand Bones
In the vast landscape of anatomical structures, the hand bones hold a prominent role due to their intricate design and essential functions in human movement and dexterity. These bones play a pivotal part in enabling the complex actions involved in grasping, manipulating objects, and carrying out fine motor tasks. The significance of hand bones goes beyond just structural support; they are fundamental in facilitating gestures, expressing emotions, and communicating non-verbally. Understanding the importance of hand bones provides insight into how these skeletal elements contribute to our daily interactions and overall well-being.
Fine Motor Skills
Hand-Eye Coordination
Hand-eye coordination is a critical component of fine motor skills, as it involves the synchronization of visual perception and hand movements to complete tasks with precision. In the context of hand bones, optimal hand-eye coordination enhances efficiency in actions that require accurate positioning and manipulation of objects. The synergy between visual input and motor output is essential for tasks such as writing, drawing, and performing intricate hand gestures. While proficient hand-eye coordination enhances productivity and skill mastery, challenges in this domain can impact overall performance and coordination.
Sensory Feedback
Sensory feedback plays a vital role in fine motor skills by providing information to the brain regarding touch, pressure, and proprioception. In the realm of hand bones, sensory feedback allows individuals to adjust grip strength, manipulate objects delicately, and navigate spatial relationships effectively. The integration of sensory information contributes to the refinement of motor skills and aids in adapting hand movements to varying tasks and contexts. Nevertheless, disruptions in sensory feedback can impair dexterity and coordination, highlighting the intricate interplay between sensory perception and motor control.
Cultural and Symbolic Importance
Gesture Communication
Gesture communication serves as a non-verbal form of expression, with hand movements conveying meanings, emotions, and intentions. In the context of hand bones, gestures play a significant role in cultural interactions, interpersonal communication, and conveying societal norms. The ability to interpret and produce gestures accurately enhances communication efficiency and fosters deeper connections across diverse communities. While gestures can bridge linguistic barriers and enrich storytelling, misunderstandings or misuse of gestures can lead to miscommunications or cultural insensitivities.
Artistic Expression
Artistic expression through hand movements encompasses a wide range of creative endeavors, including painting, sculpting, and performing arts. Hand bones provide the foundation for artists to translate their visions into tangible forms, showcasing dexterity, grace, and emotional depth. The interplay between hand bones and artistic expression reflects the intricacies of human creativity and individuality. While artistic endeavors celebrate cultural heritage and innovation, they also reveal the subtle nuances of human experiences and perspectives.
Common Hand Bone Disorders


The section on Common Hand Bone Disorders delves into essential afflictions affecting the hand's skeletal structure. Understanding these disorders is paramount for grasping the intricacies of hand bone health. By addressing conditions such as Arthritis and Fractures, the article sheds light on the challenges individuals may face in maintaining optimal hand functionality. Exploring these disorders provides a comprehensive view of the potential issues that can arise within the hand's bones, offering readers a deeper understanding of the importance of hand bone health and preventive measures to consider.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a prevalent form of arthritis that specifically targets the joints and cartilage in the hand, leading to pain and stiffness. In the context of this article, Osteoarthritis serves as a focal point due to its common occurrence and impact on hand functionality. The key characteristic of Osteoarthritis lies in its degenerative nature, gradually wearing down joint surfaces and causing discomfort. Its inclusion in this article allows for an in-depth exploration of how this disorder influences hand bones, emphasizing the need for early detection and appropriate management strategies to mitigate its effects.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis is an autoimmune condition affecting the hand's joints, resulting in inflammation and joint damage. Within the scope of this article, Rheumatoid Arthritis offers valuable insights into the complexities of immune-mediated diseases impacting hand bone health. The distinguishing feature of Rheumatoid Arthritis is its systemic nature, affecting multiple joints simultaneously and potentially leading to deformities. By examining Rheumatoid Arthritis, this article highlights the importance of recognizing and addressing autoimmune disorders that can significantly impact hand bones, providing readers with a nuanced perspective on approaches to managing this condition effectively.
Fractures and Trauma
The subsection on Fractures and Trauma explores critical injuries that can affect hand bones, interrupting their structural integrity and function. By discussing fractures such as Boxer's Fracture and Scaphoid Fracture, the article outlines the repercussions of traumatic events on hand skeletal health. This detailed analysis emphasizes the significance of prompt medical attention and appropriate interventions in addressing fracture-related challenges, underscoring the essential role of understanding common fractures in maintaining the overall well-being of hand bones.
Boxer's Fracture
Boxer's Fracture is a specific type of fracture typically occurring in the metacarpal bones of the hand, often associated with punching or impact injuries. Its significance in this article lies in its portrayal of how certain activities or incidents can lead to localized bone damage, affecting hand functionality. Highlighting Boxer's Fracture enables readers to comprehend the implications of such injuries on hand bones, stressing the importance of preventive measures and proper treatment strategies to mitigate long-term complications.
Scaphoid Fracture
Scaphoid Fracture involves a break in the scaphoid, one of the crucial carpal bones located in the hand's wrist area. Addressing this specific fracture within the article provides readers with insights into the distinctive challenges associated with wrist fractures and their impact on hand mobility. By outlining the characteristics of Scaphoid Fracture, the article underscores the necessity of accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plans to address the complexity of wrist injuries effectively, offering a comprehensive examination of traumatic occurrences affecting hand bones.
Diagnostic Approaches for Hand Bone Conditions
For comprehensive insight into the health status of the hand, diagnostic approaches play a pivotal role. Understanding the condition of hand bones requires meticulous assessment through various imaging techniques and biomechanical evaluations. In this article, we delve into the significance of diagnostic approaches for hand bone conditions, shedding light on the intricate methodologies employed to diagnose and analyze structural abnormalities or injuries.
Imaging Techniques
X-Ray
X-Ray imaging stands as a cornerstone in evaluating hand bone conditions due to its ability to penetrate tissues and provide detailed visualization of bone structures. This non-invasive technique aids in detecting fractures, deformities, or degenerative changes within the bones. While conventional X-Rays excel in showcasing skeletal anatomy, they may have limitations in depicting soft tissues. Despite this drawback, X-Ray remains a valuable tool in diagnosing hand bone issues efficiently and swiftly.
MRI
MRI offers a more comprehensive view of hand bone conditions by utilizing magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed images. This advanced imaging modality is excellent for exploring soft tissues, ligaments, and cartilage along with bone structures. Although MRI provides exceptional clarity, it can be time-consuming and costly, making it ideal for cases requiring detailed soft tissue assessment and precise diagnosis.
CT Scan
CT scans provide cross-sectional images of hand bones, offering a three-dimensional view for accurate assessment of bone abnormalities. This imaging technique excels in detecting complex fractures, joint disorders, and structural anomalies not easily visible on X-Rays. Although CT scans involve radiation exposure, the detailed insights they provide into hand bone conditions make them indispensable for thorough diagnostics.
Biomechanical Assessments
Grip Strength Testing
Grip strength testing serves as a valuable biomechanical assessment tool to evaluate the functionality and strength of hand muscles and bones. By measuring an individual's ability to grip objects forcibly, this test helps in determining muscle health and assessing conditions such as arthritis or nerve damage affecting hand functionality.
Range of Motion Analysis
Assessing the range of motion in hand joints through various maneuvers aids in identifying limitations, stiffness, or abnormalities affecting bone health. Range of motion analysis plays a crucial role in diagnosing conditions like tendon injuries, joint inflammations, or degenerative joint diseases. Understanding the flexibility and movement capabilities of hand bones is essential for devising suitable treatment plans and enhancing patient outcomes.
Treatment Modalities for Hand Bone Issues
Bones can encounter various issues that necessitate different treatment approaches. In this article, the focus is on exploring the treatment modalities specifically tailored for hand bone issues. Understanding the intricacies of these modalities is paramount in ensuring effective management and recovery. It delves into the specific elements, benefits, and considerations surrounding the treatment of hand bone issues, shedding light on the importance of comprehensive care for optimal outcomes.
Conservative Treatments

Conservative treatments form a crucial aspect of addressing hand bone disorders without resorting to surgical interventions. Among these approaches, two key elements are pivotal:
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a vital role in the rehabilitation and strengthening of hand bones. By employing targeted exercises and techniques, this modality aims to enhance flexibility, restore mobility, and alleviate pain. The essence of physical therapy lies in its ability to promote natural healing processes while minimizing the risks associated with invasive procedures. Its non-invasive nature makes it a popular choice, reflecting its efficacy in fostering recovery and functional restoration.
Bracing
Bracing serves as a supportive mechanism for providing stability to weakened or injured hand bones. This external device helps in maintaining proper alignment, reducing strain, and preventing further damage. One of the key characteristics of bracing is its customizable nature, tailoring the support to the specific needs of the individual. While offering essential protection, bracing also comes with certain limitations, such as potential discomfort or restriction of movement. Balancing these factors is crucial in harnessing the benefits of bracing for optimal outcomes.
Surgical Interventions
In cases where conservative treatments fall short or the severity of the condition demands more intensive intervention, surgical approaches become necessary. Within the realm of hand bone issues, two main types of surgical interventions are commonly employed:
Internal Fixation
Internal fixation involves the utilization of implants or devices to stabilize fractures or correct deformities within hand bones. By providing internal support, this approach allows for proper alignment and healing, reducing the risk of complications. The key characteristic of internal fixation lies in its ability to facilitate direct bone healing, leading to enhanced structural integrity. Despite its advantages, considerations regarding the potential for implant failure or infection need to be carefully evaluated.
Joint Replacement
Joint replacement surgery is a transformative intervention that aims to replace damaged or deteriorated joints with artificial counterparts. This procedure is beneficial in restoring joint function, alleviating pain, and improving overall hand mobility. The unique feature of joint replacement lies in its capacity to offer long-term relief and enhanced quality of life for individuals grappling with severe hand bone issues. However, like any surgical procedure, joint replacement comes with inherent risks and post-operative considerations that necessitate comprehensive preoperative assessment.
Nutritional Considerations for Bone Health
During the investigation of bones on hand, delving into the realm of nutritional considerations is paramount. The composition of bones relies heavily on adequate nutrition, making this topic a crucial aspect of the overarching discussion. Considering the specific elements of calcium and vitamin D, it is essential to underscore their significance in supporting bone health and integrity. Nutritional considerations for bone health encompass various benefits, such as facilitating bone growth, maintaining bone density, and preventing disorders related to bone weaknesses.
Calcium and Vitamin
Role in Bone Formation:
The role of calcium and vitamin D in bone formation stands as a cornerstone of healthy skeletal development. Calcium, known for its mineralization properties, plays a vital role in the formation and maintenance of bone tissue. Its ability to strengthen bone structure and aid in cellular functions within bones makes it a popular choice for optimizing bone health. Meanwhile, vitamin D complements calcium by enhancing its absorption and utilization in the body. Together, these nutrients work synergistically to promote bone density and overall skeletal well-being in individuals, showcasing their crucial significance in this article.
Deficiency Effects:
Conversely, the impact of deficiencies in calcium and vitamin D can lead to detrimental effects on bone health. Insufficient levels of these nutrients may result in weakened bones, increased risk of fractures, and compromised overall skeletal integrity. Addressing deficiency effects is imperative in highlighting the potential consequences of inadequate nutritional intake. Understanding the repercussions of calcium and vitamin D deficiencies underscores the importance of maintaining adequate levels of these nutrients for optimal bone health within the context of this article.
Essential Nutrients for Bone Maintenance
Exploring essential nutrients for bone maintenance reveals the substantial role of magnesium in supporting skeletal health. Magnesium, often overlooked yet vital, contributes to bone strength and density. Its unique feature lies in its involvement in over 300 enzymatic reactions in the body, promoting proper bone mineralization and metabolism. Despite its relatively lesser-known status, magnesium proves to be a critical element in maintaining robust bones. Conversely, vitamin K, renowned for its role in blood clotting, also influences bone health significantly. Its ability to regulate calcium levels in bones and prevent mineral deposition in soft tissues showcases its unique feature in supporting bone integrity. While both nutrients offer advantages in bone maintenance, understanding their respective roles and effects is crucial in optimizing bone health and emphasizing their relevance within the narrative of this article.
Future Research Directions in Hand Bone Studies
In investigating the realm of hand bone studies, future research directions play a pivotal role in shaping our comprehension of this intricate topic. The exploration towards innovative methodologies and technologies stands as a cornerstone in unraveling the mysteries surrounding hand bones. Emphasizing the significance of delving into uncharted territories, future research promises to unveil new insights that could revolutionize the field. By focusing on cutting-edge techniques and interdisciplinary collaborations, researchers aspire to enhance our understanding of hand bone structures and functions.
Bioengineering Innovations
Regenerative Medicine
In the landscape of hand bone studies, regenerative medicine emerges as a beacon of hope and breakthrough. Its unique capacity to stimulate tissue regeneration and repair offers a promising avenue for addressing various hand bone abnormalities. The key characteristic of regenerative medicine lies in its ability to harness the body's innate healing mechanisms, fostering natural recovery processes. This transformative approach not only presents a beneficial choice for advancing hand bone research but also holds the potential to redefine treatment standards. Despite its remarkable advantages, regenerative medicine also poses challenges such as regulatory hurdles and complex integration processes, underscoring the need for further exploration and refinement.
Implant Technology
Within the sphere of hand bone studies, implant technology stands out as a revolutionary intervention with multifaceted implications. The defining feature of implant technology lies in its capacity to restore structural integrity and functionalities compromised by bone disorders. This innovative solution offers a viable path for enhancing hand bone stability and function, showcasing its relevance in the context of comprehensive care strategies. While implant technology presents clear advantages in terms of efficacy and customization, it also poses risks such as implant rejection and biomechanical concerns. Therefore, a balanced evaluation of its benefits and drawbacks is essential for optimal utilization in advancing hand bone studies.
Genetic Contributions to Bone Health
Gene Therapy Advances
Envisioning the future landscape of hand bone health, gene therapy advances emerge as a groundbreaking frontier with transformative potential. The fundamental characteristic of gene therapy lies in its capability to target specific genetic anomalies underlying bone disorders, offering tailored interventions for enhanced efficacy. This specialized approach signifies a progressive choice for integrating genetic insights into the realm of hand bone research, paving the way for personalized treatment modalities. While the unique feature of gene therapy advances presents clear advantages in precision and customization, it also triggers considerations regarding long-term effects and ethical implications. Striking a balance between innovation and ethical practice is crucial in harnessing the full potential of gene therapy advances.
Precision Medicine
In the landscape of hand bone studies, precision medicine emerges as a cutting-edge paradigm with transformative implications for personalized healthcare. The hallmark characteristic of precision medicine lies in its tailored approach that considers individual variability in genes, lifestyle, and environment. This personalized framework represents a significant leap forward in optimizing diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for hand bone conditions, reflecting a paradigm shift towards individualized care. Despite its tremendous advantages in treatment efficacy and patient outcomes, precision medicine necessitates careful consideration of data privacy and accessibility challenges. Navigating the complexities of precision medicine requires a nuanced approach that prioritizes patient well-being while advancing the frontiers of hand bone research.







